Our Market
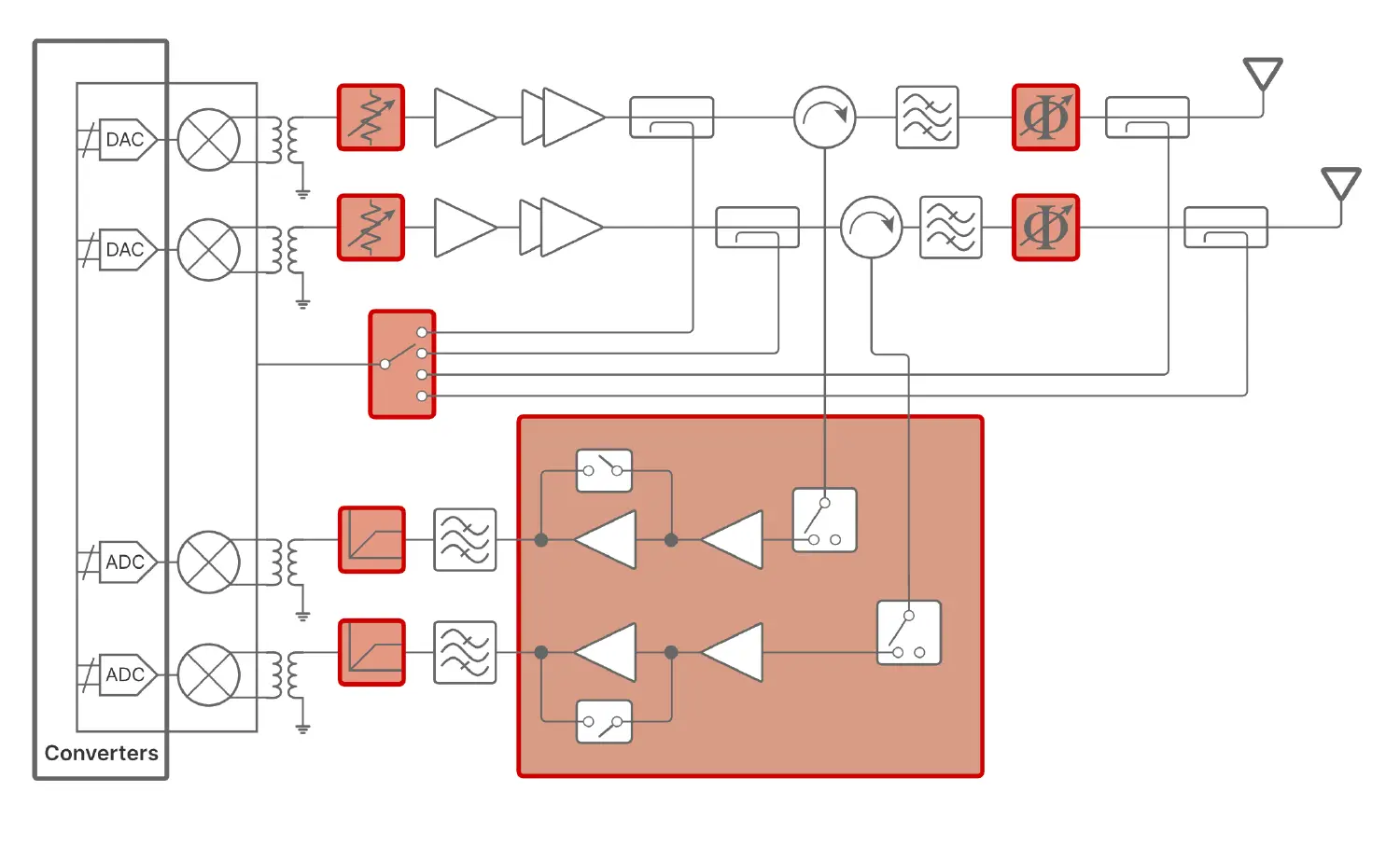
Cellular Networks
Macro and Small-Cells
- Best-in-class RF performance
- Low power consumption
- Small form factor integration in both FR1 and FR2 bands
- Enabling beamforming, MIMO and other 5G techniques
pSemi Products for Mobile Include



Communication Infrastructure
Expanded LTE and 5G Network Capacity
The combination of an increasing global subscriber base, expansion of advanced wireless networks and the proliferation of powerful devices offering high-speed wireless internet access has dramatically increased mobile data traffic.
This increase is straining the existing wireless network infrastructure. As a result, operators are expanding their network capacity by acquiring additional wireless spectrum and by aggressively deploying long term evolution (LTE), time division-LTE (TD-LTE) and 5G New Radio (5G-NR) networks.
Communication Infrastructure
LOS and NLOS for Wireless Backhaul Flexibility
Wireless backhaul is one of many options to connect the base station to the core network, and, as data consumption grows, so does the need for high-speed backhaul. Line of sight (LOS) microwave solutions are used extensively and offer high data rate wireless backhaul solutions.
With the rollout of small cells in urban environments where LOS is not always simple to achieve, non-line of sight (NLOS) solutions are being deployed, which offer lower data rates but can be used to increase the flexibility of the backhaul deployment.